
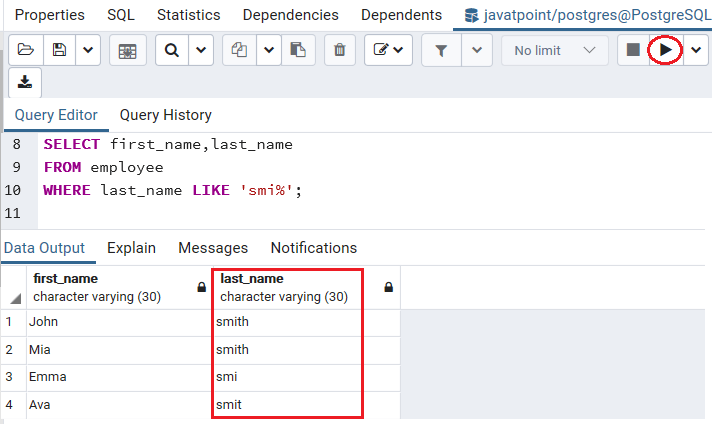
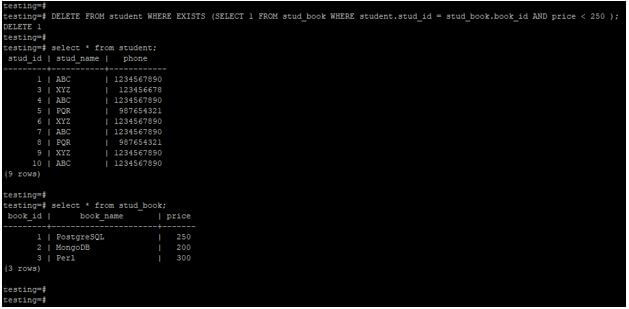
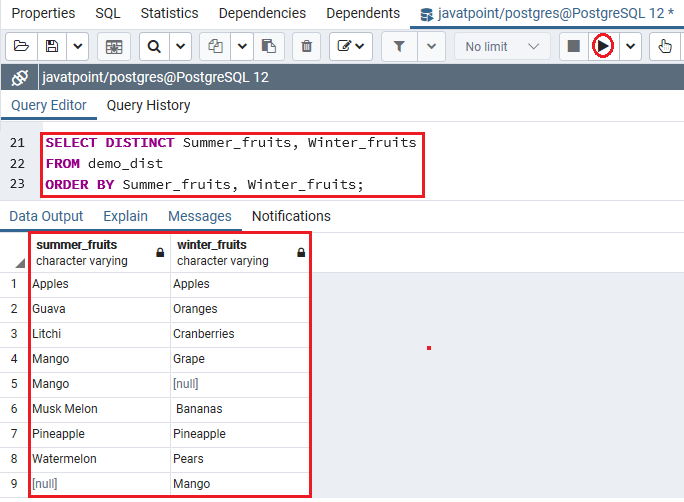
~: matches against a pattern using POSIX regular expressions, case sensitive.SIMILAR TO: matches against a pattern using SQL's regular expression dialect.ILIKE: matches against a pattern (using the wildcards % to match 0 or more characters and _ to match a single character), case insensitive.LIKE: matches against a pattern (using the wildcards % to match 0 or more characters and _ to match a single character).EXISTS: the query that follows contains results.NOT: negates the boolean value that follows.BETWEEN: value is contained within the range the minimum and maximum values that follow, inclusive.IN: value is contained in the list, series, or range that follows.OR: logical "or" operator - joins two conditions and returns TRUE if at least one of the conditions are TRUE.AND: the logical "and" operator - joins two conditions and returns TRUE if both of the conditions are TRUE.In PostgreSQL, a boolean value is any of TRUE, FALSE, or NULL.Ĭonditions are often formed using one or more of the following operators: The can be anything that results in a boolean value. The basic syntax of the WHERE clause looks like this: If the result of the expression is true, it satisfies the criteria of the search and will continue on for any further processing as a candidate row. If the result of the expression is false, the row will be removed from the results and will not be returned or continue to the next stage of processing. WHERE clauses work by defining boolean expressions that are checked against each candidate row of data. The WHERE clause lets you define actual search criteria for query statements by specifying conditions that must be true for all matching records. One of the most common and broadly useful ways to indicate your query requirements is the WHERE clause. Using the WHERE clause to define match criteria
#Postgres in clause how to#
We will show how to test against characteristics within individual records with WHERE clauses, how to group records together to summarize information with GROUP BY, how to filter groups of records with the HAVING subclause, and how to set the maximum number of returned rows with the LIMIT clause. In this guide, we will take a look at some of the most common filtering operations available within PostgreSQL and demonstrate how to use them to narrow the focus of your statements. By using filtering clauses within your queries, you can add specific criteria in order to return only the most relevant records. To work with data in a database, you need to be able to retrieve and target specific records effectively.

#Postgres in clause update#
How to update existing data with SQLite.How to perform basic queries with `SELECT` with SQLite.Inserting and deleting data with SQLite.Creating and deleting databases and tables with SQLite.Profiling and optimizing slow queries in MySQL.
Using joins to combine data from different tables in MySQL.How to perform basic queries with `SELECT` in MySQL.An introduction to MySQL column and table constraints.How to create and delete databases and tables in MySQL.Introduction to optimizing PostgreSQL performance.Using joins to combine data from different tables in PostgreSQL.How to filter query results in PostgreSQL.How to perform basic queries with `SELECT` in PostgreSQL.An introduction to PostgreSQL column and table constraints.An introduction to PostgreSQL data types.How to create and delete databases and tables in PostgreSQL.How to configure a PostgreSQL database on RDS.Comparing relational and document databases.Glossary of common database terminology.Comparing database types: how database types evolved to meet different needs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
